Strange–Rahman–Smith equation
The Strange–Rahman–Smith equation is used in the cryoporometry method of measuring porosity. NMR cryoporometry [1][2][3] is a recent technique for measuring total porosity and pore size distributions. NMRC is based on two equations, the Gibbs–Thomson equation, that maps the melting point depression to pore size, and the Strange–Rahman–Smith equation [1] that maps the melted signal amplitude at a particular temperature to pore volume.
Equation
If the pores of the porous material (of diameter  ) are filled with a liquid, then the volume of the pores
) are filled with a liquid, then the volume of the pores 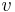 at a particular pore diameter may be obtained from the melting point in the pores
at a particular pore diameter may be obtained from the melting point in the pores 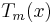 by [1] :
by [1] :
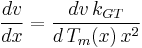
Where: 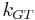 is the Gibbs–Thomson coefficient for the liquid in the pores.
is the Gibbs–Thomson coefficient for the liquid in the pores.
References
- ^ a b c Strange, J.H.; Rahman, M.; Smith, E.G. (Nov 1993), "Characterization of Porous Solids by NMR", Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 (21): 3589–3591, Bibcode 1993PhRvL..71.3589S, doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.71.3589, PMID 10055015, http://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevLett.71.3589
- ^ Mitchell, J.; Webber, J. Beau W.; Strange, J.H. (2008), "Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Cryoporometry", Phys. Rep. 461: 1–36, Bibcode 2008PhR...461....1M, doi:10.1016/j.physrep.2008.02.001
- ^ SE-10044 Stockholm Sweden. [Furo Istvan Royal Inst TechnolDiv Phys Chem Dept Chem SE-10044 Stockholm Sweden. Royal Inst Chem SE-10044 Stockholm Sweden. [Furo Istvan] Royal Inst Technol Technol Ind NMR Ctr Dept Chem SE-10044 Stockholm Sweden. Div Phys Chem Dept Chem SE-10044 Stockholm Sweden. Royal Inst], "NMR cryoporometry: Principles applications and potential"